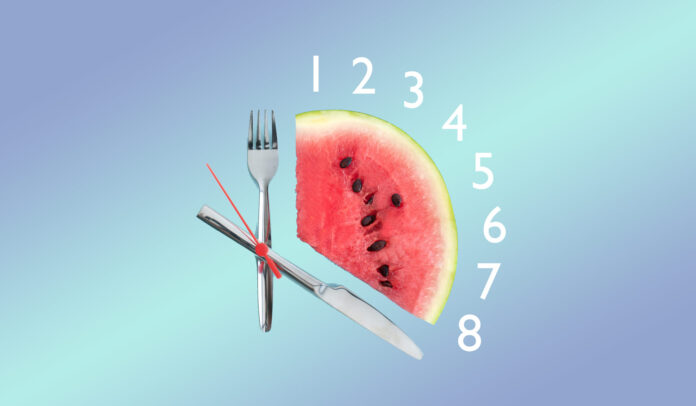
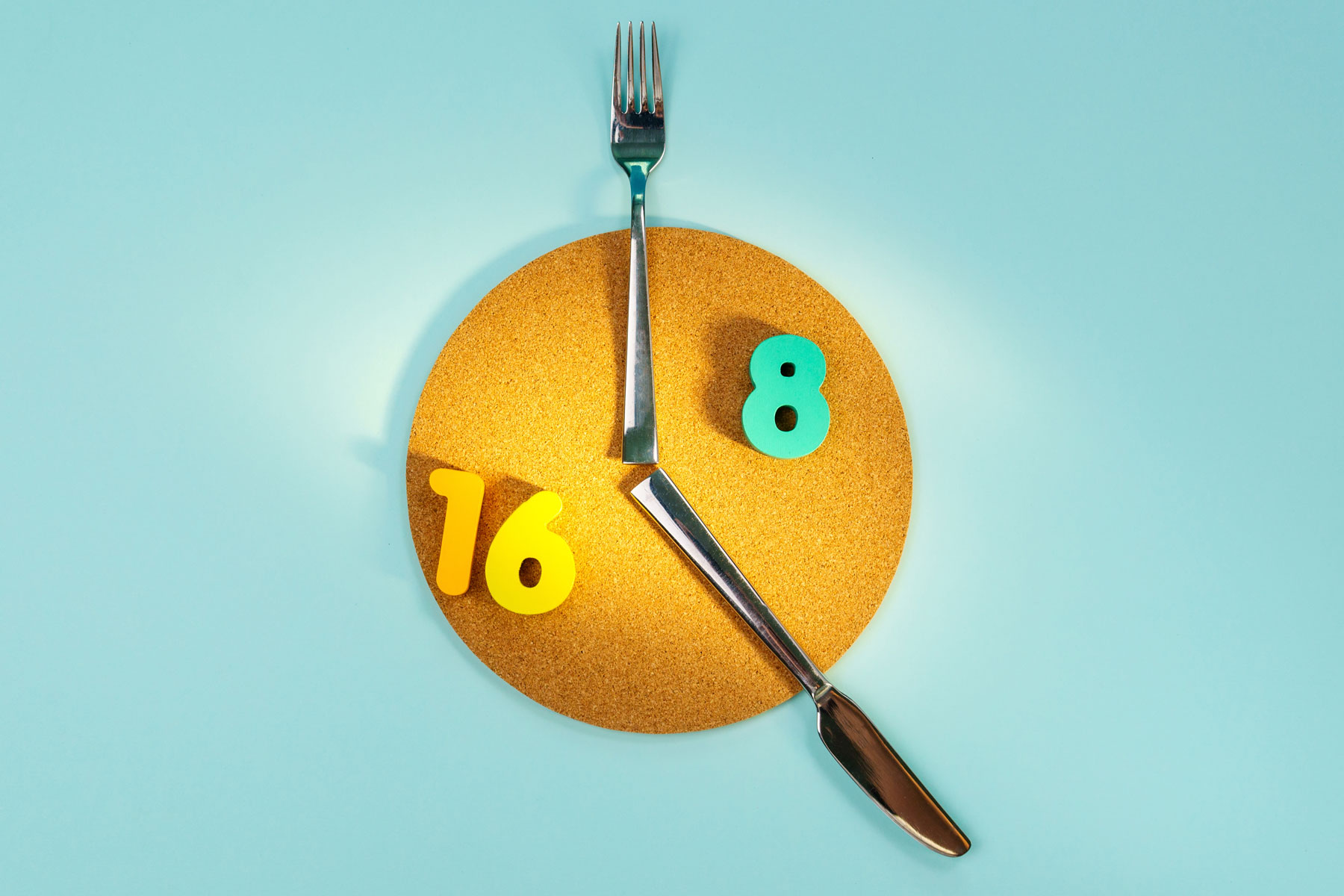The term “interval fasting” does not accurately describe the essence of such eating – it is more correct to use the term “food window.” Studies emphasize separately that the 8-hour period of food intake is a conditional interval, not a clear rule.
The mechanics of the experiment are one of the main reasons why interval fasting (“the 16/8 diet”) is based on an 8-hour window of food intake. This was the interval¹ of feeding the experimental mice that was easiest given the length of the lab technicians’ workday.
Modern research (already on humans, not mice) has been critical of recommending exactly 8 hours – noting that a number of opinions on interval starvation are flawed. Plus, the replacement phrase “feeding window” – or “food window” – is increasingly mentioned in the scientific literature.
Evolutionary Theory of Nutrition.

Biologists believe² that for thousands of years people did not have free access to food–that is, food was eaten periodically as it was found. Plus, it was probably very rarely consumed at night and late into the evening – in the absence of electricity, people simply slept.
However, modern statistics² show that the average eating time for most people is more than 12 hours – and for 50% of the population the figure exceeds 15 hours. In fact, we are talking about eating almost 24 hours a day.
Yet, more and more scientists are saying that such eating patterns can have a negative effect on metabolism – hypothesizing³ that eating should be limited to a period of about 8-12 hours (implying not eating at night, and eating a fairly early dinner).
Who invented interval fasting?
The first study¹ of the effects of interval fasting on metabolic parameters was published in 2012. Despite the fact that many traditional practices involve fasting to some extent, the issue has not been previously studied in terms of its effect on metabolism.
A key finding of the aforementioned study was that mice who ate at random times were more prone to developing obesity and impaired insulin production – compared to mice who ate during the 8-hour food window. The caloric intake was the same.
Based on this study, the idea of 16/8 interval fasting – sometimes called the “16/8 diet” – became widespread.
The food window – what is it?

If the logic of the term “interval fasting” is based on refusal to eat, then the term “food window” is its mirror image. That is, the food window refers to the period when food is consumed-as opposed to the time that implies starvation.
The food window does not stop at the point at which you stop chewing the last piece of food for the day. Smaller portions of food are digested faster than larger portions-and it can take up to 4-5 hours for the body to fully digest incoming food.
In fact, when a certain person decides to stick to a 16/8 interval fasting schedule (i.e., 16 hours of not eating and 8 hours of eating) – given the time to digest the food would be going about the 14/10 or even the 13/11 regime.
How correct is the term “fasting”?
Unfortunately, in practice interval fasting is often misunderstood – people literally mean fasting with drastic calorie restrictions.
It’s important to understand that the logic of interval fasting is not based on calorie restriction – but on controlling the amount of time food is consumed (implying large portions).
This is why the term “food window” is increasingly being used in the scientific literature – which more correctly captures the essence of the issue.
What’s the best eating schedule?

Although the data link too long of a food window with health risks – there are no definite recommendations about its “normal” duration and there can’t be.
For example, impaired insulin production and malfunctions in blood sugar regulation impose limits on one’s ability to get by without eating – requiring more frequent meals.
Practical guidelines
The results of studies on interval fasting and food windows often contradict typical dietitian recommendations (e.g., questioning the benefits of eating small meals in small portions).
Many of the claims are still just theories with no clear evidence base. However, the basic recommendations can be summarized in the following points:
- Don’t eat after dinner-apparently in the evening even small amounts of carbohydrates can provoke a significant metabolic response.
- Don’t eat in the first hours after waking up – it is increasingly suggested that the body needs time in the morning hours to transition into digestion mode.
- Stick to a stable eating regimen – try to eat around the same time, which will allow the body to adapt its metabolic cycles.
- Stick to your chosen regimen long enough – it probably takes up to a few weeks for your body to adjust to a certain eating schedule.
The term “interval fasting” does not accurately describe the essence of such eating; it is more correct to use the term “food window. Studies separately emphasize that the 8-hour period of food intake is a conditional interval, not a clear rule.
Sources:
- Time restricted feeding without reducing caloric intake prevents metabolic diseases in mice fed a high fat diet, source
- The when of eating: The science behind intermittent fasting, source
- Time-Restricted Eating to Prevent and Manage Chronic Metabolic Diseases, source
Read also:
- How do I check my gastrointestinal function?Stomach pain, constipation or diarrhea, bloating, belching, heartburn? These are all symptoms of problems in the gastrointestinal tract. It starts with the mouth and esophagus and ends with the intestines and rectum.
- What are the benefits of hazelnut oil for the skin?Hazelnut oil is rich in vitamins and essential fatty acids that nourish the skin. Here are a few reasons why you should add this oil to your skin care routine.
- Immune-boosting aromatic oilsThere are many products and treatments that can help your body to build a natural resistance to the harsh winter months, and aromatherapy is one of them. There are many studies supporting the healing power of aromatherapy and it is good for both mental and physical health. Aromatic essential oils also have many health benefits… Read more: Immune-boosting aromatic oils
- Marula Oil Benefits, Uses, and PrecautionsMarula Oil is an exotic oil that comes from the African Marula tree. It’s a good ingredient for skin, hair, and nails. Learn more about the benefits and precautions of Marula Oil with our guide.
- Goal setting for students, children and young peopleRemember when you learned how to set goals? If you have trouble answering this question, you are not alone! Most of us don’t spend much time thinking about how we set our goals. In fact, many of us don’t even think of goal setting as a skill; rather, it’s something we do without much thought.… Read more: Goal setting for students, children and young people
The articles on this site are for information purposes only. The site administrators are not responsible for attempting to apply any recipe, advice or diet, nor do they guarantee that the information provided will help or harm you personally. Be cautious and always consult a doctor or nutritionist!
*All products recommended are selected by our editorial team. Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, you help us earn a small commission from the seller and thus support the writing of useful and quality articles.