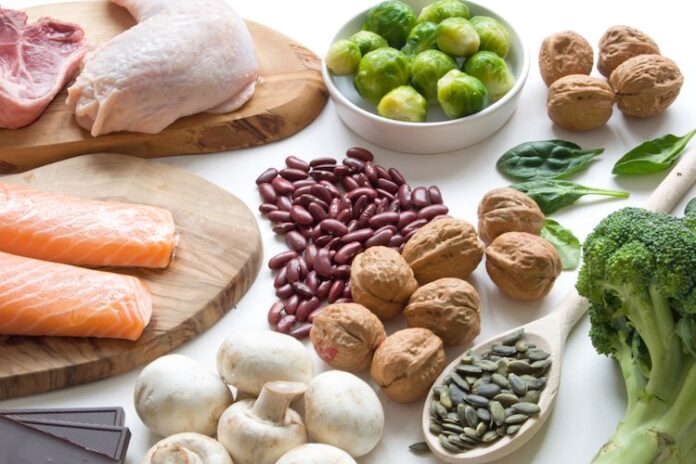
Iron is a vital mineral, and deficiency of iron is associated with fatigue, dizziness, headaches and poor concentration. Long-term low intake of this mineral can lead to the development of anaemia.
In the following article you will find out what iron is, how iron deficiency manifests itself and in which foods it is found most abundantly.
What is iron and what effect does it have on health
In Latin it is called Ferrum (Fe), in English the word iron is used, and it is responsible for many important functions in the human body. The optimal amount in the body is around 4 grams, which is not too much, yet many people suffer from a deficiency.
Iron is a component of of the blood pigment hemoglobin a muscle dye myoglobin and is essential for the transport of oxygen from the lungs to cells, tissues and muscles. It is found in many body organs and enzymes. Optimal levels of iron in the body are essential for heart and muscle function, tissue growth, blood formation and prevention of anemia, as well as immune system function.
Main effects of iron:
- Supports the nervous system and the body’s defenses.
- It improves concentration, memory, reduces exhaustion and adds natural color to the skin.
- Helps transport oxygen from the lungs to all tissues.
- Promotes growth.
- It is important for respiration.
- It plays an essential role in blood formation.
- It has a significant effect on the proper function of the immune system.
- It protects the body from the action of free radicals.
- Helps maintain the quality of skin, hair and nails.
- Furthermore, iron affects cognitive function, promotes concentration, is required for the activation of a variety of enzymes, and serves as a catalyst for various reactions.
Recommended daily intake of iron
The recommended daily intake depends on age, sex and body condition. Pregnant women, adolescent girls and boys, and menstruating women need increased iron intake.
Iron is extremely important for a child’s development and growth from birth. In the elderly, iron deficiency is usually associated with inadequate nutrition or more difficult mineral absorption in general.
The main source of minerals should always be a balanced and varied diet. Proper iron intake should be a priority:
- women during menstruation,
- expectant mothers,
- postpartum women.
Recommended daily doses of iron:
| Age | DZR |
| Within 12 months | 6,2 mg |
| Children 1 to 10 years | 3.9 to 5.9 mg |
| Girls 11 to 14 years old before menstruation | 9.3 mg |
| Girls 11 to 14 years after menstruation | 21.8 mg |
| Girls 15 to 17 years old | 20.7 mg |
| Pregnant and lactating women | 20 to 30 mg |
| Pre-menopausal women | 19.6 mg |
| Women during menopause | 7.5 mg |
| Boys 11 to 17 years old | 9.7 to 12.5 mg |
| Men 17 years and over | 9.1 mg |
Recommended values for vegetarians:
| Gender and age | DZR |
| Teenage girl | 26 mg |
| Adult female | 33 mg |
| Boys and men | 14 mg |

Health problems caused by iron deficiency
Iron deficiency is usually caused by inappropriate and poor dietary composition, adherence to strict and unilateral diets or fasting, but also by ill-considered adherence to vegetarian and vegan dietary rules. Women are more likely to suffer from lower iron levels during menstruation and pregnancy, when consumption of this mineral rises sharply.
The cause may also be higher blood loss due to heavier menstruation and diseases such as uterine tumors, hemorrhoids, kidney and urinary tract damage, stomach ulcers, etc.), or impaired iron absorption.
Occasional fluctuations do not matter, but long-term iron deficiency can have a detrimental effect on health. The first symptoms tend to be subtle at first and usually involve irritability, general fatigue and exhaustion as the blood is not sufficiently oxygenated and the body lacks energy.
The most common manifestations of iron deficiency are:
- fatigue and exhaustion,
- impaired ability to concentrate,
- irritability,
- nausea,
- shortness of breath even without increased physical exertion,
- tingling in the calves,
- motor restlessness (restless legs syndrome),
- breathing difficulties and dizziness, dizziness and headaches,
- aphthae and cracked corners, sore mouth,
- conspicuously pale skin, dry skin,
- paleness of conjunctivae, gums and nail beds,
- increased hair breakage and nail fraying,
- whistling in the ears,
- chills,
- swelling of the lower and upper limbs,
- unreasonable weight loss,
- heavy and painful menstruation in women,
- easier formation of bruises and petechiae,
- anaemia (sideropenic anaemia = iron deficiency anaemia).
What does anemia mean
It is a reduced concentration of hemoglobin in the blood, impaired ability of the blood to deliver oxygen to the tissues, and impaired red blood cell production. It is manifested by fatigue, malaise, weakness, dizziness, impaired concentration, flatulence, weight loss, shortness of breath and chest pain on exertion, feelings of severe palpitations, paleness of the skin and mucous membranes, and other manifestations (see above).
Risks of iron overdose
Excessive intake can also cause health problems. Iron is deposited in the tissues and, if too much is taken over a long period of time, can lead to damage to the heart, liver or pancreas. The maximum daily intake of iron is 45 mg. There is a risk of overdose especially with inappropriate overuse of vitamin supplements.
Common manifestations of higher intake:
- Heartburn,
- nausea and vomiting,
- diarrhea or constipation,
- pressure in the abdomen,
- depression,
- joint pain,
- development of neurodegenerative diseases.
Caution should be exercised against excessive use of dietary supplements containing iron, repeated blood transfusions, or consumption of large amounts of meat and other animal products.
Iron-rich foods
Iron is one of the essential nutrients that the body cannot produce on its own and therefore needs to be taken in food. However, it is not a rare mineral and is found in a wide variety of foods, both animal and plant.
The difference lies in the absorption of the mineral. Animal products contain heme iron, which has an absorption rate of 10 to 30%, and plant products non-heme iron with a lower absorption rate of about 5 to 10%. Iron from animal sources is therefore absorbed much better than from plant sources.
This is also the main reason why vegetarians and vegans are at risk of iron deficiency, and why they should emphasize the quality of sources and take dietary supplements with iron.
However, foods of plant origin have a much higher concentration of iron in them. In addition, fruits and vegetables also contain vitamin Cwhich is very important for iron absorption.
Iron deposition is also promoted by folic acid and copper. A complication is the combination of iron with calcium, fiber, and tannins found in tea and coffee. For this reason, it is not ideal to consume foods containing large amounts of iron, dairy products together and wash them down with coffee or tea.
The best sources of iron in food
- Meat, offal and other animal products: Beef, lamb, chicken, rabbit, veal, beef, chicken and pork liver, eggs,
- Fish: cod, tuna, salmon,
- vegetables: Lettuces, spinach, arugula, field greens, kohlrabi, beets, broccoli, asparagus, cabbage, celery, leeks, lettuce,
- fruit: Strawberries, raspberries, blackcurrants, grapes, blackberries, figs, avocados, apricots, cherries, sour cherries, blueberries, plums, pears, dates,
- dried fruits: Apricots, plums, raisins, goji,
- dried mushrooms
- legumes: Lentils, beans, chickpeas, peas, soybeans,
- cereals: Oatmeal, wheat bran, whole wheat and spelt flour, rye, barley, corn, rice,
- nuts and seeds: Pistachios, cashews, almonds, hazelnuts, Brazil nuts, pine nuts, coconut, pumpkin and sunflower seeds,
- green foods: chlorella, spirulina and young barley,
- Other: dark chocolate, yeast.
Table of selected foods containing iron:
| Food | Quantity in 100 g |
| Dried porcini mushrooms | 6.9 mg |
| Dried yeast | 17.5 mg |
| Soy | 1,5 mg |
| Liver | 1.5 mg |
| Lentils | 1.5 mg |
| Poppy | 1.5 mg |
| Cocoa | 8 mg |
| Leek | 7,5 mg |
| Egg yolks | 7 mg |
| Pistachios | 6.8 mg |
| Sunflower seeds | 6.7 mg |
| Chickpea | 6 mg |
| Peas | 4.5 mg |
| Beef | 3 to 5 mg |
| Oatmeal | 3.8 mg |
| Spinach | 3.3 mg |
| Chicken meat | 1.8 to 3.2 mg |
| Raisins | 2.6 mg |
| Figs | 2.6 mg |
| Dark chocolate | 2.4 mg |
DO YOU KNOW Red and purple colored foods contain higher amounts of iron? That is why it is recommended to eat, for example, strawberries, cherries, blackcurrants, beetroot, red cabbage, red potatoes or red meat when you are deficient in iron. Spinach is far from the best source of this mineral.

Dietary supplements with iron
As long as your diet is varied enough and includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, good quality meats and healthy fats, you should have no problem getting the recommended amount of iron and other minerals daily.
But if you’ve been iron deficient for a long time or are expecting a baby, don’t shy away from quality supplements. A haematologist can help you choose the best one, by carrying out blood tests, assessing your current state of health and recommending the best way to supplement iron without worrying about your health or that of your baby.
Final summary: Iron is especially important for young girls, pregnant and breastfeeding women
What should you remember about iron?
- It is essential for the formation of hemoglobin, myoglobin, and the activation of a variety of enzymes.
- Iron from animal products is better absorbed than from plant materials.
- For adequate intake, it is advisable to consume cereals, legumes, vegetables, fruits and meat.
- Iron deficiency initially manifests itself only in fatigue, irritability and poorer ability to concentrate.
- Excess iron cannot be eliminated by the body. Beware of taking dietary supplements and eating large amounts of animal products.
Read also:
- How do I check my gastrointestinal function?Stomach pain, constipation or diarrhea, bloating, belching, heartburn? These are all symptoms of problems in the gastrointestinal tract. It starts with the mouth and esophagus and ends with the intestines and rectum.
- What are the benefits of hazelnut oil for the skin?Hazelnut oil is rich in vitamins and essential fatty acids that nourish the skin. Here are a few reasons why you should add this oil to your skin care routine.
- Immune-boosting aromatic oilsThere are many products and treatments that can help your body to build a natural resistance to the harsh winter months, and aromatherapy is one of them. There are many studies supporting the healing power of aromatherapy and it is good for both mental and physical health. Aromatic essential oils also have many health benefits… Read more: Immune-boosting aromatic oils
- Marula Oil Benefits, Uses, and PrecautionsMarula Oil is an exotic oil that comes from the African Marula tree. It’s a good ingredient for skin, hair, and nails. Learn more about the benefits and precautions of Marula Oil with our guide.
- Goal setting for students, children and young peopleRemember when you learned how to set goals? If you have trouble answering this question, you are not alone! Most of us don’t spend much time thinking about how we set our goals. In fact, many of us don’t even think of goal setting as a skill; rather, it’s something we do without much thought.… Read more: Goal setting for students, children and young people
The articles on this site are for information purposes only. The site administrators are not responsible for attempting to apply any recipe, advice or diet, nor do they guarantee that the information provided will help or harm you personally. Be cautious and always consult a doctor or nutritionist!
*All products recommended are selected by our editorial team. Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, you help us earn a small commission from the seller and thus support the writing of useful and quality articles.