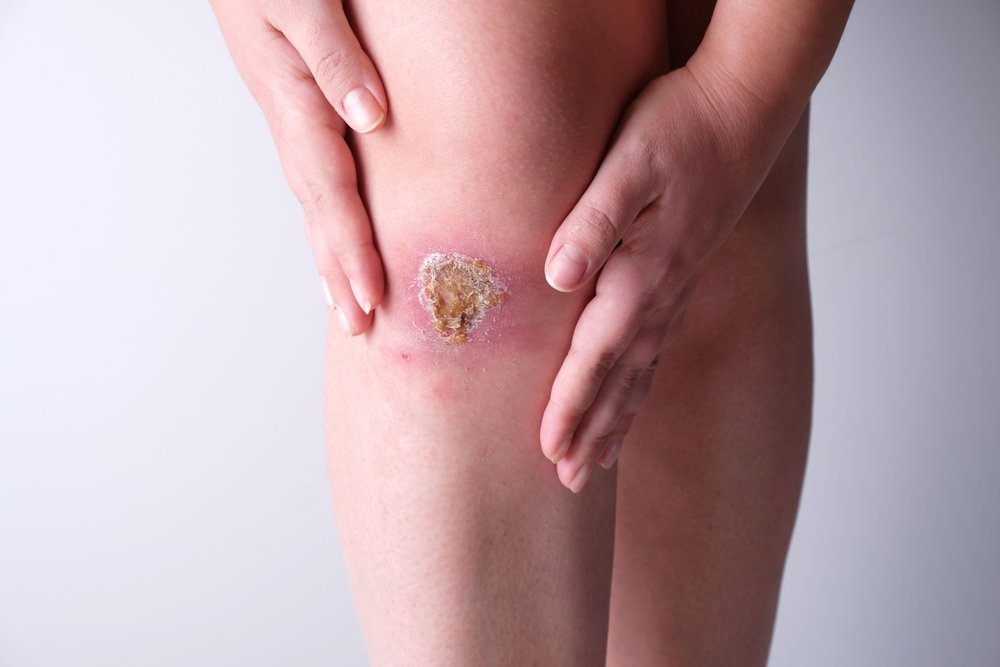
As you know, a wound is any violation of the integrity of the skin and underlying tissues as a result of mechanical traumatic effects on them. Every year millions of people of all ages visit trauma centers because of wounds of one or another localization.
In some cases, tissue damage is even a reason for hospitalization (with extensive or complicated wounds). In this article we will talk about the course of the wound process and secondary healing.
The healing process of wound defects
The wound process refers to the phenomena that occur in a wound from the time it appears until it is completely healed.
To date, it is customary to distinguish three stages of wound healing:
- Inflammation;
- regeneration;
- Epithelialization.
The inflammation stage begins at the moment of tissue damage and, in the absence of any complications, lasts about four or five days. Initially there is spasm of vascular structures, thrombosis, followed by expansion of small vessels. There are phenomena of exudation with release of plasma proteins, migration of blood cells to the lesion. There occurs prolapse of fibrin threads.
As a result of increased osmotic pressure in tissues edema develops, the surrounding tissues are infiltrated. Clinically, this stage is manifested by edema and reddening of the lesion site.
The second stage, as we have already said, is called regeneration. Its average duration is from two to four weeks. Signs of edema and exudation decrease. There is an active formation of new collagen, new blood and lymphatic vessels are formed, the place of tissue defect is filled with granulation tissue.
The last stage is epithelialization. Its duration can vary considerably, which will be determined by the depth and area of tissue damage. During this period the wound defect is closed with epithelium, starting from the edges, moving towards the central part. In parallel, connective tissue matures and a scar is formed.
Types of healing
There are three main types of wound defect healing:
- Healing by primary tension is the most favorable option, usually found in surgical, noninfected wounds. It occurs when the edges are even, the distance between them is not more than one centimeter. There is no suppuration and an even, linear scar is formed.
- Wound healing by secondary tension is the overgrowth of the wound site through suppuration. In this case the wound defect is filled with granulation tissue with subsequent fibrosis and epithelialization, and formation of a rough scar. This variant is usually found in septic wounds, which was proved by scientists from the A.I. Evdokimov Moscow State University of Medicine and Dentistry in a paper published in 2018. Secondary tension healing occurs when there are extensive tissue defects, foreign bodies, or necrotic tissue in the wound.
- Healing under the scab occurs when the integrity of the superficial layers of the skin is compromised (the growth layer is not affected). In this case a scar is not formed, the wound defect tightens under the crust.
The articles on this site are for information purposes only. The site administrators are not responsible for attempting to apply any recipe, advice or diet, nor do they guarantee that the information provided will help or harm you personally. Be cautious and always consult a doctor or nutritionist!
*All products recommended by thefirstdoc.com are selected by our editorial team. Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, you help us earn a small commission from the seller and thus support the writing of useful and quality articles.