When you go to any medical center, whether it is a paid clinic or a state institution, the examination plan for pregnancy planning will be approximately the same, based on developed standards. In order to successfully carry a pregnancy to term, it is necessary to first examine and eliminate the detected abnormalities in health.
The diagnostic program includes general tests and examinations for hormones, infections and some pathologies, as well as ultrasound of endometrium, reproductive organs and breasts, followed by generalization of the data by a doctor to develop a scheme of correction, treatment and further preparation for conception.
Pregnancy planning: a sample examination plan
If we talk about the approximate scheme that applies during the period of pregnancy planning, it includes some procedures and examinations, according to the data of which it is possible to get an idea of the general state of health and the functioning of the reproductive system in particular.
Thus, pregnancy planning necessarily involves a visit to a gynecologist or a specialist in planning, as well as general tests and ultrasound of the endometrium and the entire genital area, and if necessary – and the breast. In addition, a gynecological examination includes colposcopy with collection of material for cytology (examination of cervical cells for neoplasia).
Also required are examinations to detect various intimate infections, smears and cultures from the cervix to determine the composition of microbial flora.
If planning a pregnancy against the background of existing health problems, both reproductive and other, involves testing for hormones (genital, thyroid, if necessary – adrenal glands), as well as counseling and treatment by subspecialty doctors.
How to assess a woman’s readiness for conception with the new SPERO-screen analysis
When you’re planning a pregnancy you always want to know whether or not it will work, how long to try, what the chances of success are. You can, of course, ask your doctor, but it is very difficult to give a prognosis. Everyone has different biological rhythms.
Even the healthiest couple is known to conceive within 12 months. This is the norm as defined by the WHO. But now it has become possible to estimate the likelihood of pregnancy individually with a new laboratory test SPERO-screen You can get a hormone test by filling out a questionnaire and taking a blood test for hormones.
The study gives a prognosis for the next 3 menstrual cycles in the form of a numerical expression – the SPERO index. The higher it is, the higher are the chances of pregnancy.
The new study differs from the “conventional” hormone test in that the results are correlated with history data, and using complex mathematical calculations, a fertility window (days when conception is most likely) and an index are determined to estimate the probability of pregnancy in the current and 2 immediate cycles.
Conducting ultrasounds of the endometrium, genitals, and breasts
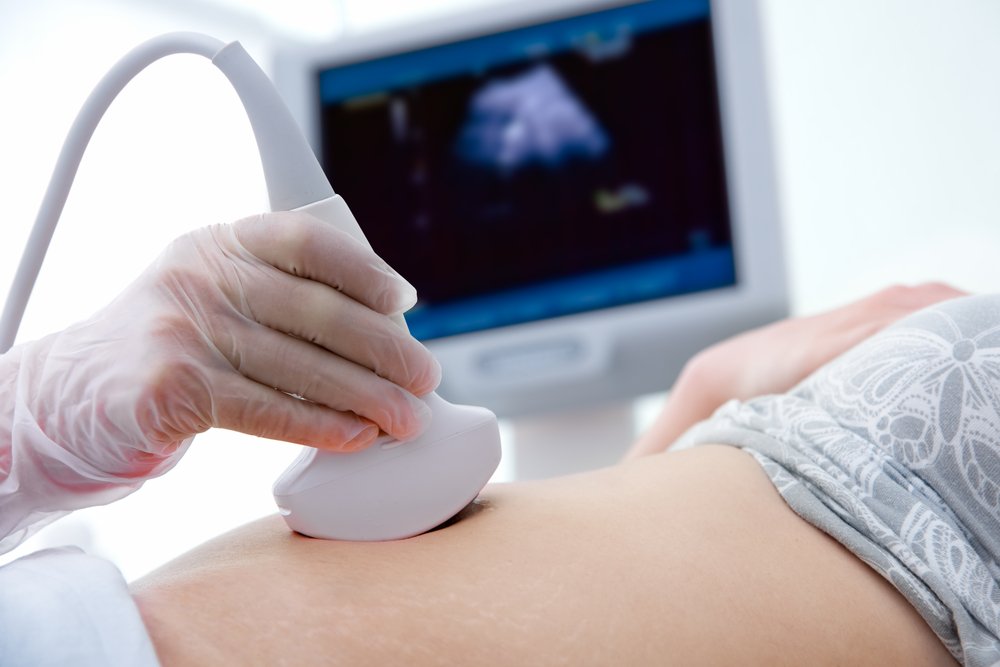
When planning a pregnancy, routine ultrasounds of the endometrium, cervix and corpus uteri, ovaries and urinary organs are prescribed to evaluate the structure and functionality of the reproductive organs and associated systems.
By examining the ovaries, the presence of follicles in the ovaries is assessed, including maturing follicles, which allows for pregnancy. If there are problems with hormonal background or ovarian function, the structure of the internal wall of the uterus, USG of the endometrium and ovaries is performed in dynamics, assessing the increase in layer thickness and degree of follicle development.
If abnormalities are detected, their correction is carried out with the assessment of ultrasound endometrium and follicles in the dynamics, in certain phases of the cycle under the influence of treatment.
Without sufficient thickness of the inner layer of the uterus and follicle maturation, pregnancy will not occur. In addition, according to the data obtained in the dynamics of ultrasound of the endometrium and follicle size, the doctor will calculate the most successful days for conceiving a baby.
Effects on pregnancy of various abnormalities and their detection
Abnormalities in the structure of the genitals, especially the uterus and cervix, as well as inflammatory changes in the ovarian area, cysts or neoplasms can significantly affect the onset of pregnancy and its further course.
In addition, various uterine pathologies – tumors (myomas), scars, endometriosis and other pathological processes – affect pregnancy. To detect them, an ultrasound examination is carried out during the planning period, usually on the 5 to 8 days of the monthly cycle. If necessary, Dopplerometry is also indicated to assess the blood flow in the uterine vessels, especially if there are scars after surgery or myomatous nodes.
It is important to examine the mammary gland, which undergoes serious structural changes during pregnancy, which can be dangerous if there are lumps or tumors inside the gland. It is especially important to undergo an ultrasound scan if your breasts are sore or your lymph nodes are enlarged, or if there are nodules or lumps in the structure.
General tests and special investigations
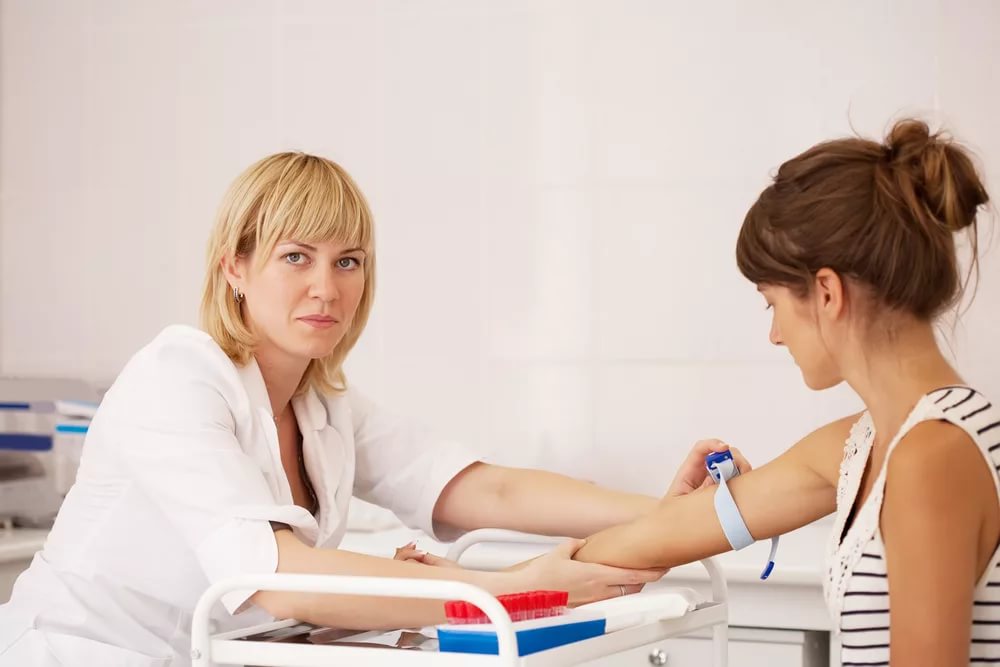
The examination package includes a number of general tests, which include primarily blood tests to rule out HIV and hepatitis, as well as syphilitic lesions, group and Rh factor testing to rule out possible blood and Rh factor conflicts with the fetus.
Blood tests for TORCH infections are performed at least two to three months before conception. These include rubella, toxoplasma, cytomegaly and herpes.
When antibodies to these infections are detected, preventive measures to prevent and treat these pathologies must be taken.
If antibodies to cytomegaly and herpes are detected, the level of M or G immunoglobulins must be determined separately, which is important to determine the risk of infecting the fetus during pregnancy.
If viral activity is detected, the doctor will prescribe a course of therapy to suppress the activity of the process. In the absence of antibodies to rubella in the blood, the expectant mother should be immunized against rubella, since infection with this virus in early pregnancy leads in many cases to fetal abnormalities and defects.
General tests are performed:
- Biochemical blood test with determination of the main indicators reflecting the work of the digestive and many other systems of the body. This test can indicate serious metabolic disorders.
- Clotting blood test (coagulogram) with determination of clotting factors and time to correct a condition of increased clotting or decreased clotting in time. A tendency to clotting can significantly complicate the course of pregnancy, so it is necessary to treat such an abnormality in advance.
- General blood and urine tests – allow you to identify somatic or infectious diseases of the woman, allergic and other pathologies. It is especially important to detect urinary infections, anemia or liver abnormalities. This will exclude pathologies such as pyelonephritis, cystitis, and intestinal microbial flora disorders during pregnancy.
- A stool test for helminths is also performed.
Physician Consultation
Many women have many different pathologies by the time they plan to become pregnant – dental caries, tonsillitis, maxillitis, pyelonephritis and cystitis, skin infections or some other pathology. All of them require complete treatment, so that they do not exacerbate during pregnancy. Their treatment requires consultation with specialized specialists, to whom the gynecologist refers the woman for advice and possible treatment.
Major Consultants:
- Therapist.
- Ophthalmologist,
- Dentist,
- ENT doctor.
Consultations with all other specialists may also be scheduled, if necessary.
Hormone study

If there are thyroid problems, menstrual irregularities, breast problems, or long periods of infertility, hormones, both sex hormones and some others, are examined. Ovarian, pituitary, and adrenal hormones (sex hormones – androgens, estrogens) influence conception and conception.
In addition, thyroid hormones have an impact, and all of them need to be carefully examined and adjusted during the planning period.
Source:
- http://icmr.nic.in/annual/2004-05/nirrh/11%20Chapter%207%20Genetic%20Disorders.pdf
- http://www.indiaparenting.com/genetic-testing/430_4049/when-is-genetic-testing-done-in-pregnancy.html
- http://www.checkpregnancy.com/sensitive-pregnancy-tests-2015/
- http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/pregnancy-and-baby/pages/screening-tests-abnormality-pregnant.aspx
- http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/healthlibrary/conditions/pregnancy_and_child birth/common_tests_during_pregnancy_85,P01241/
- http://www.babycenter.com/0_carrier-screening-for-inherited-genetic-disorders_1453030.bc
http://www.livescience.com/45949-prenatal-genetic-testing.html - http://health.ccm.net/contents/300-tests-carried-out-during-pregnancy
The articles on this site are for information purposes only. The site administrators are not responsible for attempting to apply any recipe, advice or diet, nor do they guarantee that the information provided will help or harm you personally. Be cautious and always consult a doctor or nutritionist!
*All products recommended by thefirstdoc.com are selected by our editorial team. Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, you help us earn a small commission from the seller and thus support the writing of useful and quality articles.





