
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are referred to as essential. This means that the human body can do without them, but cannot make them. Both are important, but an excess of omega-6s can lead to health problems. It is best to maintain a healthy balance of intake while choosing appropriate sources.
Omega-6 fatty acids are just as important to humans as omega-3s. However, the recommendation is to maintain a healthy intake and not to overdo it. Knowing what omega-6 acids are, how they work and which foods contain them will help to better understand them.
What are omega-6 fatty acids and why are they needed
Omega-6 fatty acids are needed by the human body for a wide range of processes and functions, such as cell membrane formation, reproduction and nerve tissue construction. Since the body cannot make them on its own, it must take them in through the diet.
They are found in some vegetable oils, such as:
- sunflower oil,
- rapeseed oil,
- soybean oil,
- corn oil,
- palm oil,
- sesame oil.
It belongs to the group polyunsaturated fatty acids and their main representative is linoleic acid (CLA). Omega-6 acids also include Arachidonic acid (AA) a gammalolenic acid (GLA), but which the human body can synthesize from CLA.
Fatty acids are very different from ordinary fats. They are not stored and used by the body as an additional source of energy. Once ingested from the diet, they remain biologically active in the body and participate in many bodily processes including normal immune system functions, blood clotting, and more.
How omega-6 acids affect health
In the right levels, omega-6 fatty acids help to lower blood fat levels, increase good cholesterol (HDL) and promote anti-inflammatory processes.
For example, conjugated linoleic acid in the form of a dietary supplement can help reduce fat a not to increase the level of inflammatory markers. Gamalinolenic acid, found in evening primrose oil and borage oil, may reduce the symptoms of inflammatory conditions.
But excessive intake has the opposite effect and can lead to the development of diseases of civilization. Increased intake of omega-6 fatty acids can cause problems in the form of chronic inflammation. It is one of the main causes of diseases of civilization, such as heart disease, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, arthritis, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, and others.
Long-term omega-6 excess can result in:
- Poor permeability and absorption of hormones and nutrients,
- insufficient metabolism at the cellular level,
- impaired natural detoxification process of the organism,
- the formation of a pro-inflammatory environment in the cells,
- difficulty concentrating and learning, and impaired memory,
- more frequent mood swings.
Summarized:
Omega-6s have pro-inflammatory effects a omega-3 anti-inflammatory. Diets with predominant omega-6 and low omega-3 intake increase inflammation. Conversely, a diet based on a balanced intake of omega-3 and omega-6 reduces inflammation.
Differences between omega-6 and omega-3 and their ideal ratio
Long-term excess omega-6 acids can harm health. They can raise blood fat levels and have have a pro-inflammatory effect. The latter is important for the protection of the organism, as they induce an acute inflammatory reaction that contributes to wound healing. Omega-3 acids have anti-inflammatory effect, help lower blood pressure, blood clotting and promote healthy brain, heart and blood vessels.
For omega-6 fatty acids to be as beneficial, it is necessary to reduce their intake and instead focus on a higher intake of omega-3s. Translated into more understandable language, consume less vegetable oils and more fish and seafood.
In fact, the main problem of society and its nutrition lies in the excessive intake of omega-6 acids at the expense of omega-3 acids. The intake of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids in the ratio of 2:1 to 3:1. However, the actual ratio of fatty acids in the common Western diet varies in a ratio of 16:1 or more.
Diets with a significant predominance of omega-6 increase the risk of cardiovascular, inflammatory, autoimmune and cancer diseases. This is also why contemporary society is so often faced with cardiovascular diseases, which are one of the most common causes of death.
How to maintain a balanced ratio of omega-6 and omega-3 acids in your diet
The first step to correcting this is to limit foods rich in omega-6 acids, and increase your intake of foods containing omega-3 acids.
Include oily fish, seafood, flax and hemp seeds or nuts in your diet, and limit highly processed foods. Always choose quality ingredients. Humans need both. If they are in balance, your heart, blood vessels, brain and immune system will function better.
Basic advice on how to achieve a balanced fatty acid intake:
- Eat fish once, preferably twice a week.
- In addition to regular vegetable oils, use omega-3 rich oils. Olive oil is the best known.
- Limit your consumption of fried foods and unhealthy fast food.
- Don’t be afraid to take dietary supplements with pure omega-3s. This is especially true if you don’t eat fish or seafood.

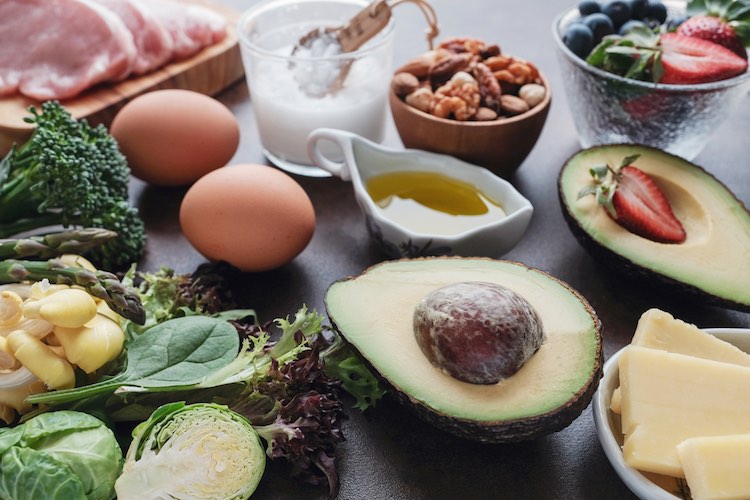
Foods containing omega-6 fatty acids
The largest amounts of omega-6 are found in refined vegetable oils. This includes dishes prepared on them. Nuts and seeds also contain larger amounts.
Omega-6 acid content of selected foods:
| Food | Quantity |
| Walnuts | 7.5 g in 20 g |
| Safflower oil | 7.18 in 10 ml |
| Sunflower seeds | 5,36 g in 20 g |
| Almonds | 4.5 g in 20 g |
| Hemp seeds | 4 g in 20 g |
| Tofu natural | 3,9 g in 100 g |
| Peanut butter | 1.8 g in 10 ml |
| Cashew | 1,45 g in 20 g |
| Avocado oil | 0.99 g in 10 ml |
| Eggs | 0,48 g in 1 pcs |
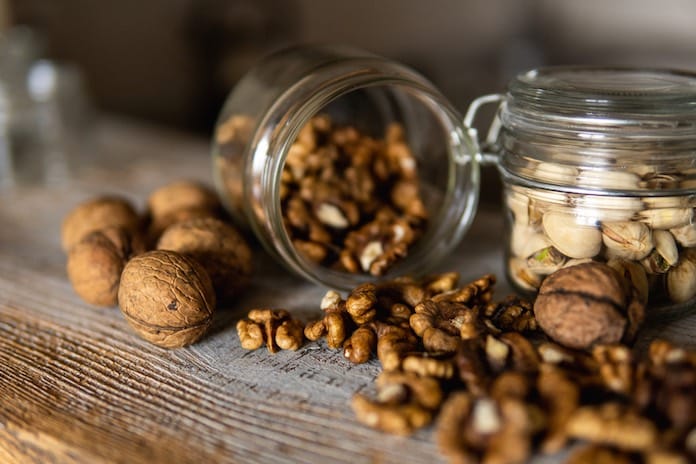
Walnuts
In addition to omega-6 acids, the popular walnuts contain essential fibre or minerals for digestion, especially manganese, copper, phosphorus and magnesium. They can be eaten on their own for snacks, added to breakfast muesli and porridge, yoghurt or vegetable salad.

Safflower oil
This lesser-known type of cooking oil is extracted from the oil seeds of safflower and, like other vegetable oils, contains higher amounts of monounsaturated fats, which, according to this study promote heart health. Its flavor is neutral and it is suitable for use in baked goods, salad dressings and sauces.
Sunflower seeds
Sunflower seeds contain a large number of vitamins and minerals including selenium and vitamin E. These are powerful antioxidants that protect the body from cell damage and the development of chronic diseases. Their mild nutty flavour and crunchy texture make them ideal for adding to salads, homemade granola, muesli mixes and healthy bars.
Almonds
They are an excellent source of protein, fiber, vitamin E, manganese and magnesium. You can enjoy them on their own as a healthy snack, but they are also suitable for desserts and breakfast cereals.
Hemp seeds
They contain a large amount of fats beneficial to the heart and vascular system. In addition, they are a great source of protein, vitamin E, phosphorus and potassium. Hemp seeds are good in porridges, yoghurt, smoothies, muesli and salads.
Tofu
Vegetable cheese is made by curdling soy milk and then pressing it into soft blocks that are easy to cut. Each serving of tofu provides the human body with a hearty dose of key nutrients including protein, iron, calcium and manganese. Tofu is added to salads, vegetable pancakes or used as a vegetable alternative to meat in main courses.
Peanut butter
The delicious creamy spread is made from roasted peanuts. It is rich in healthy fats and proteins, vitamin E, vitamin B3 (niacin), manganese and magnesium. Its use is versatile. It can be spread on whole wheat bread, used as a dressing on fruit or vegetable salad, or blended into a smoothie.
Cashews
Cashew nuts are characterized by their buttery taste and original shape. They are rich in micronutrients including copper, magnesium and phosphorus. If you soak and blend them beforehand, you get a smooth cashew cream that is suitable for sauces, soups and homemade dressings.
Avocado oil
Contains antioxidants and benefits the heart and vascular system. Its great advantage is its high smoke point, which allows it to withstand high temperatures without breaking down and oxidizing. It is therefore also suitable for high temperature cooking such as baking, roasting and frying.
Eggs
They are a nutritious and versatile food containing many important nutrients such as protein, selenium and riboflavin. They are prepared in various ways (boiled, omelette) and added to batters of savoury and sweet dishes.
How about vegetable oils high in omega-6
In the case of vegetable sources, it is recommended to focus on commonly used cooking oils and not limit yourself to one type.
More suitable than the commonly used sunflower oil, which contains only minimal amounts of omega-3, is the better rapeseed oilwhose ratio of omega-3 and omega-6 is much more balanced. A good source of omega-3 is also flaxseed oil, which is suitable for cold dishes as a dressing for salads and sweet dishes. Don’t forget animal fats such as butter and lard.
Overview of oils with higher omega-6 content:
- sunflower oil
- safflower oil
- corn oil
- soybean oil
- peanut oil
Oils with a balanced ratio of omega-6 and omega-3 are preferable:
- coconut oil
- olive oil
- rapeseed oil
- linseed oil
- butter and ghee
- lard
Keep in mind that fats lower in omega-6 are unhealthy in larger amounts, especially animal fats. So always use fats wisely.

Food supplements with fatty acids.
Combination omega fatty acid supplements provide sufficient amounts in appropriate ratios, i.e. 2:1. These products help to increase omega-3 intake and thus improve the balance of fatty acids in the body.
However, most people take in optimal amounts of omega-6 as part of their normal diet. It is therefore preferable to take supplements containing only omega-3 fatty acids, which are generally deficient in people’s diets.
Final summary: Give your body the right amount of fatty acids
Excess omega-6 fatty acids increase the risk of chronic inflammation. It is therefore important to maintain a balance in your omega-6 and omega-3 intake, which should ideally be 2:1 or 3:1. Our bodies need both types, you just need to be careful how much you consume.
What you should remember:
- Use vegetable and animal oils that contain both omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Use canola oil or other oils with a balance of omega-3 and omega-6 acids instead of sunflower oil for cooking and frying.
- Have fatty fish rich in omega-3 acids preferably twice a week.
- Limit your consumption of fried foods and unhealthy fast food.
- Include supplements with omega-3 fatty acids in your diet.
- Don’t be afraid to take dietary supplements with pure omega-3s. This is especially true if you do not eat fish and seafood.
Read also:
- How do I check my gastrointestinal function?
 Stomach pain, constipation or diarrhea, bloating, belching, heartburn? These are all symptoms of problems in the gastrointestinal tract. It starts with the mouth and esophagus and ends with the intestines and rectum.
Stomach pain, constipation or diarrhea, bloating, belching, heartburn? These are all symptoms of problems in the gastrointestinal tract. It starts with the mouth and esophagus and ends with the intestines and rectum. - What are the benefits of hazelnut oil for the skin?
 Hazelnut oil is rich in vitamins and essential fatty acids that nourish the skin. Here are a few reasons why you should add this oil to your skin care routine.
Hazelnut oil is rich in vitamins and essential fatty acids that nourish the skin. Here are a few reasons why you should add this oil to your skin care routine. - Immune-boosting aromatic oils
 There are many products and treatments that can help your body to build a natural resistance to the harsh winter months, and aromatherapy is one of them. There are many studies supporting the healing power of aromatherapy and it is good for both mental and physical health. Aromatic essential oils also have many health benefits… Read more: Immune-boosting aromatic oils
There are many products and treatments that can help your body to build a natural resistance to the harsh winter months, and aromatherapy is one of them. There are many studies supporting the healing power of aromatherapy and it is good for both mental and physical health. Aromatic essential oils also have many health benefits… Read more: Immune-boosting aromatic oils - Marula Oil Benefits, Uses, and Precautions
 Marula Oil is an exotic oil that comes from the African Marula tree. It’s a good ingredient for skin, hair, and nails. Learn more about the benefits and precautions of Marula Oil with our guide.
Marula Oil is an exotic oil that comes from the African Marula tree. It’s a good ingredient for skin, hair, and nails. Learn more about the benefits and precautions of Marula Oil with our guide. - Goal setting for students, children and young people
 Remember when you learned how to set goals? If you have trouble answering this question, you are not alone! Most of us don’t spend much time thinking about how we set our goals. In fact, many of us don’t even think of goal setting as a skill; rather, it’s something we do without much thought.… Read more: Goal setting for students, children and young people
Remember when you learned how to set goals? If you have trouble answering this question, you are not alone! Most of us don’t spend much time thinking about how we set our goals. In fact, many of us don’t even think of goal setting as a skill; rather, it’s something we do without much thought.… Read more: Goal setting for students, children and young people
The articles on this site are for information purposes only. The site administrators are not responsible for attempting to apply any recipe, advice or diet, nor do they guarantee that the information provided will help or harm you personally. Be cautious and always consult a doctor or nutritionist!
*All products recommended are selected by our editorial team. Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, you help us earn a small commission from the seller and thus support the writing of useful and quality articles.